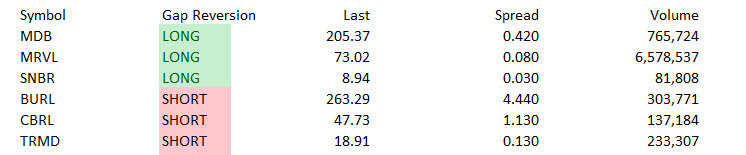
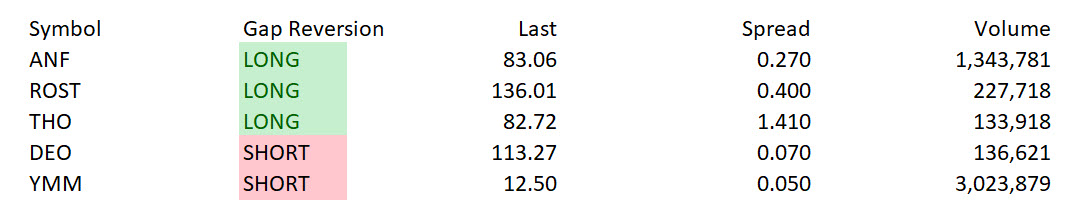
The Small Cap Swing Trader Alert Archive
Below you'll find The Small Cap Swing Trader setups stacked up and ordered chronologically.March 6, 2025
How Germany Raising Its Debt Limit for Defense Impacts the Global Defense Industry
Germany’s Defense Budget Surge: A Game Changer for the Industry
Germany raising its debt limit for defense marks a turning point in European military strategy. As global security threats rise, Germany has committed to significantly increasing its military spending. This decision could impact the global defense industry, driving demand for advanced weapons systems, cybersecurity infrastructure, and strategic alliances.
The Financial Times has recently covered how Germany’s increased defense spending aligns with NATO commitments and geopolitical shifts. With a growing emphasis on deterrence and force modernization, German military contracts could provide new opportunities for global defense firms.
Why Germany Is Raising Its Debt Limit for Defense
In response to rising geopolitical tensions, particularly in Eastern Europe and the Indo-Pacific, Germany is expanding its military budget beyond its constitutional debt brake. This move is partly driven by pressure from NATO allies, who have long urged Germany to meet its 2% GDP defense spending commitment.
By increasing its defense spending, Germany aims to:
- Modernize its armed forces with next-generation weapons and cybersecurity tools
- Enhance NATO’s collective security and fulfill alliance obligations
- Strengthen its domestic defense industry, reducing reliance on foreign suppliers
- Support European strategic autonomy in military operations
For investors and defense industry leaders, this shift signals a wave of new contracts, partnerships, and innovations.
Global Defense Industry Benefits from Germany’s Military Expansion
Germany raising its debt limit for defense presents a significant opportunity for major defense contractors, including Airbus, Rheinmetall, and Lockheed Martin. As Germany moves to update its military infrastructure, several key sectors are poised to benefit:
1. Weapons Manufacturing and Procurement
With an expanding budget, Germany will likely invest in state-of-the-art fighter jets, naval ships, and missile defense systems. Defense giants like Rheinmetall are expected to see an uptick in contracts for armored vehicles and munitions.
2. Cybersecurity and Electronic Warfare
As modern conflicts increasingly involve cyber threats, Germany’s defense upgrades will emphasize network security and intelligence operations. This could benefit cybersecurity firms specializing in military-grade encryption and AI-driven threat detection.
3. Drone and Autonomous Weapons Development
Germany’s defense expansion will also include drone technology and automated battlefield solutions, creating opportunities for companies specializing in unmanned systems.
4. Defense Stocks and Market Growth
The increased military spending could boost European defense stocks for traders and investors. Explore strategies for capitalizing on defense sector investments at traderinsight.com.
Strategic and Economic Implications of Germany’s Military Growth
While Germany raising its debt limit for defense strengthens NATO and European security, it also raises economic and political concerns.
- European Economic Impact – Increased military spending may divert funds from social programs, affecting public services.
- Geopolitical Reactions – Russia and China could perceive Germany’s military expansion as an escalation, influencing global defense strategies.
- Investment Considerations – Traders and investors should monitor the financial implications of Germany’s defense spending.
Final Thoughts: What’s Next for the Defense Industry?
Germany raising its debt limit for defense is a strategic shift with long-term consequences. As the country accelerates military upgrades, defense firms stand to benefit from increased procurement contracts and R&D funding. Investors should watch defense stocks closely, as rising military budgets could create lucrative opportunities in the global arms market.
How tariffs drive price volatility in U.S. manufacturing stocks
How Tariffs Drive Price Volatility in U.S. Manufacturing Stocks
When headlines shift from earnings beats to tariff threats, manufacturing stocks often become the first casualties. The U.S. industrial sector, heavily reliant on global supply chains and predictable input costs, is uniquely exposed to tariff-driven shocks. Understanding how tariffs drive price volatility in U.S. manufacturing stocks is essential for traders navigating an increasingly politicized economic landscape.
A Chain Reaction: From Tariffs to Stock Swings
Tariffs act like a tax on business inputs. When the U.S. government imposes duties on foreign goods — such as Chinese steel, semiconductors, or EV components — manufacturers must either absorb the cost or pass it along to consumers. Neither path is appealing.
For example, when the Trump administration announced sweeping new tariffs in 2025, Ford Motor Co. immediately suspended its forward guidance, citing a projected $1.5 billion hit. The result? Shares tumbled, and the auto sector followed. Read more here.
This is a textbook case of how tariffs drive price volatility in U.S. manufacturing stocks — not just through earnings pressure, but by injecting uncertainty into future forecasts, supply chains, and capital expenditure decisions.
Why Manufacturing Is Especially Sensitive
- Thin Margins: Many industrial firms operate on tight margins, and sudden input cost increases can quickly erode profitability.
- Global Supply Chains: Components are often sourced globally. Tariffs on intermediate goods can disrupt production or delay delivery timelines.
- Forecasting Risk: Companies like Caterpillar, Boeing, and General Motors rely on long-term planning. When tariff policy changes overnight, it undercuts confidence in multi-year growth outlooks.
- Investor Sentiment: The market tends to punish uncertainty. Even well-managed firms can see stock prices fall sharply after tariff announcements — especially if forward guidance is withdrawn or revised downward.
Case Studies: Market Reactions to Tariffs
- Ford (2025): As discussed, Ford’s $1.5B tariff burden prompted a suspension of guidance and a selloff in shares. This caused broader weakness across the automotive sector.
- Caterpillar (2018): During the original U.S.-China trade war, CAT dropped over 15% in just a few weeks as investors feared rising steel costs and falling Chinese demand.
- Whirlpool (2018): Initially expected to benefit from tariffs on imported washers, Whirlpool saw higher steel and aluminum costs hurt margins — leading to a post-earnings slide of 14%.
These examples show clearly how tariffs drive price volatility in U.S. manufacturing stocks, regardless of whether a company is a direct target or caught in the ripple effect.
What Traders Should Watch
- Official Announcements: Presidential orders, USTR releases, and WTO rulings can move markets within minutes.
- Input Cost Indicators: Commodity prices (steel, aluminum, rare earths) often forecast the impact before earnings do.
- Forward Guidance Changes: Watch for manufacturers that withdraw guidance or warn about uncertainty — these are high-probability volatility events.
- Sector ETFs: Funds like XLI (Industrial Select Sector SPDR) often show early signs of institutional sentiment shift.
Conclusion
Understanding how tariffs drive price volatility in U.S. manufacturing stocks is no longer optional — it’s a trading edge. Whether you’re swing trading major industrial names or scalping news-based momentum, recognizing the cause-and-effect link between tariff policy and price action can improve your timing, risk management, and trade selection. In a market where headlines can move billions, awareness is profitability.
March 5, 2025
Tariffs Impact on Auto Supply Chain
How the Tariffs Impact on Auto Supply Chain Could Trigger a Trade War
The Immediate Effect of Tariffs on the Auto Industry
The tariffs impact on auto supply chain is set to cause significant disruptions across North America. With the United States imposing new duties on imports from Canada and Mexico, automakers face rising costs, potential layoffs, and production delays. Given that auto components frequently cross borders multiple times before assembly, any new trade barrier creates inefficiencies and adds to the already mounting expenses in an industry struggling with high post-pandemic vehicle prices.
Why the Auto Supply Chain is Particularly Vulnerable
The auto industry operates on a just-in-time manufacturing model, meaning parts arrive precisely when needed to minimize storage costs. Tariffs disrupt this process in multiple ways:
- Higher production costs: Analysts estimate that tariffs could increase vehicle prices by as much as $3,000 per unit (WSJ).
- Border delays: Customs processing for tariffed goods can slow down supply chains, causing production bottlenecks.
- Job losses: The auto sector relies on free trade agreements like USMCA to remain competitive. If costs rise, manufacturers may cut jobs or relocate production.
Other Industries at Risk
The tariffs impact on auto supply chain is not the only economic concern. Several other industries face similar vulnerabilities:
Energy Sector
Canada is a major supplier of crude oil to the U.S. If tariffs lead to retaliatory duties on energy, fuel prices could surge, impacting consumers and businesses alike (RSM).
Agriculture
Farmers are heavily reliant on exports, especially to China and Mexico. Tariffs on steel, aluminum, and machinery raise production costs, while retaliatory tariffs on soybeans, corn, and pork limit market access.
Technology
Electronics manufacturing relies on global supply chains. Tariffs on semiconductor imports from Asia could increase costs for consumer electronics, cloud computing, and automotive chips.
What This Means for Traders and Investors
The tariffs impact on auto supply chain could lead to increased volatility in auto stocks, especially for companies with heavy North American operations such as Ford (NYSE: F) and General Motors (NYSE: GM). Supply chain disruptions may also impact tech and consumer goods stocks.
Related Posts on TraderInsight.com:
- How U.S.-China Tariffs Impact the Stock Market: What Investors Need to Know
- Trump Tariffs Market Impact: What Traders Need to Know Before Monday’s Open
- Trump’s Canada-Mexico Tariffs: What Traders Need to Know
Conclusion
The tariffs impact on auto supply chain is just the beginning of a potential full-scale trade war that could have ripple effects across multiple industries. Investors should monitor market reactions and be prepared for increased volatility. With supply chain disruptions looming, now is the time to reassess trading strategies and look for opportunities in a shifting economic landscape.


